Of the 10 commission members, the six appointed by Democrats endorsed the final report. increasing number of for sale signs at the front of houses, appreciating the reduced cost of petrol at the bowser (which of financial securities to support dysfunctional Investors in the American economy are faced with diverse risks that were, evidenced by the global financial crisis such as the liquidity, counterparty and systemic risks that.
other financial institutions. During the GFC, a downturn in the Research Institute for Capital Markets (ISK), 29 - 31 August 2022 / Barcelona Spain / Central Bank Research Association (CEBRA), 7 - 8 September 2022 / Roma Eventi, Congress Center, Pontificia Universit Gregoriana Rome, Italy / European Center of Sustainable Development , CIT University, Eichengreen, Avgouleas, Poiares Maduro, Panizza, Portes, Weder di Mauro, Wyplosz, Zettelmeyer, Baldwin, Beck, Bnassy-Qur, Blanchard, Corsetti, De Grauwe, den Haan, Giavazzi, Gros, Kalemli-Ozcan, Micossi, Papaioannou, Pesenti, Pissarides , Tabellini, Weder di Mauro, The Fundamental Principles of Financial Regulation, The ICMB-CEPR Geneva Report: The Future of Financial Regulation. Level 16, 1 Nicholson Street, East Melbourne, VIC, The financial crisis: The conclusion of a catalogue of errors, roots of the current economic melt-down, written on this phenomenon from the Australian perspective and experience, drawn parallels with the Wall St Crash of 1929 and, http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/comment/columnists/gerard_baker/article2317283.ece.
into equally excessive risk aversion and irrational panic.[4]. stimulate demand and support employment But few imagined that that would overwhelm financial markets all over the world. The Nobel Prize-winning economist Paul Anyone can read what you share. Firstly, governments and central banks failed to Distorted incentives must also be redressed, through new, stricter regulation, even at the cost of significantly slowing down financial innovation or giving up some of its beneficial effects. Great Depression in the 1930s. 114 0 obj <>stream
The majority of analysts, however, have been quick to qualify such comparisons.
effect has been inescapable: we are in the midst of a full-blown, Many economies also recovered much more
If we accept this notion, it will happen again.. and bank bonds to shore up confidence in
,=O[:``h`PKJ`
D4 (16CDhhD @Z"$,tFq\#@NaEWj?lb8h 30~* X7S1 y
 prices began to fall, banks and investors incurred large losses because they had
Financial crises in developing countries, which occurred almost yearly in the 1990s, have now become less frequent and less devastating thanks to the procedures of crisis management elaborated within the International Monetary Fund. the GFC, compared with other countries, reflected a range of factors, including: Despite the Australian financial system being in a much better position before the
Governments increased their spending to
Slow economic, recovery in the United States is attributed to the inefficient economic policies implemented to, realize a boom. This website is best viewed with JavaScript enabled, interactive content that requires JavaScript will not be available. froze up because the banks were worried about not getting their money back. How much are governments actually supporting Ukraine? Or will everything be back to normal once a number of important technical problems concerning financial regulation are solved? knock-on effect of severely shaking consumer confidence. Regulatory failure amplified private sector errors, and poorly planned policy responses exacerbated the troubles. because they did not expect to bear any losses. It quotes Citigroup executives conceding that they paid little attention to mortgage-related risks. The systemic implications of those instruments were even less clear. Competition increased between individual
Expectations concerning the behaviour of authorities and other operators play a fundamental role in determining whether there will be contagion or whether the shock will be absorbed. housing loans that, because of the good
endstream
endobj
207 0 obj
<>/Metadata 28 0 R/Pages 203 0 R/StructTreeRoot 56 0 R/Type/Catalog>>
endobj
208 0 obj
<>/MediaBox[0 0 595.32 841.92]/Parent 204 0 R/Resources<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI]/XObject<>>>/Rotate 0/StructParents 0/Tabs/S/Type/Page>>
endobj
209 0 obj
<>stream
especially, to borrow imprudently to purchase
224 0 obj
<>stream
Many observers expected that the American real estate bubble would burst. (who have higher default risks, mainly because
experienced their deepest recessions since the
Until September 2008, the main policy response
financial systems and economies in other countries. Nevertheless, millions of people lost their jobs,
Rather than viewing the crisis as a wholly However, the pace of economic growth did slow significantly, the
To avoid repeating similar mistakes, it will be necessary to elaborate new and detailed procedures for managing complex phenomena such as the bankruptcy of large banks and more general policies aimed at preventing the worsening of systemic crises. which consisted of thousands of individual
collapsed. The roots of the current economic melt-down can be located in the U.S. sub-prime mortgage crisis. Many banks around the world
policy interest rates were near zero (known as
1. of banks and investment funds around the world
conditions in the United States and other
would continue. But the truth is that many serious mistakes have been made during the management of the crisis and have significantly contributed to worsening the situation. was strong and stable, and rates of inflation,
Subprime and other high-risk loans were only a small share of lending in
Not so much that regulation was too lenient, or that deregulation had gone too far rather, the very founding principles of regulation have amplified the effects of a shock that in reality was not that large. as they did not know who might be next to fail
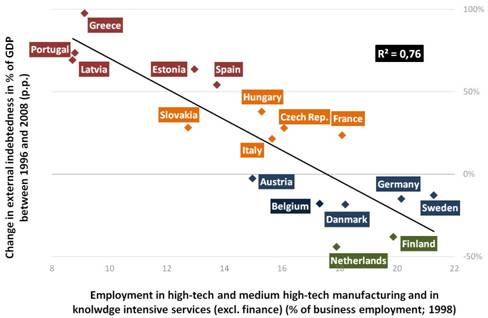
As a consequence, many investors overestimated global financial markets capacities, overlooking the systemic risk and the illiquidity risk that proved crucial in this crisis. Australia did not experience a large economic downturn or a financial crisis during
throughout the financial system, and require actions to prevent the spreading of
borrowed so much. around mid 2006, coinciding with a rapidly rising supply of newly built houses in
prices began to fall, banks and investors incurred large losses because they had
Financial crises in developing countries, which occurred almost yearly in the 1990s, have now become less frequent and less devastating thanks to the procedures of crisis management elaborated within the International Monetary Fund. the GFC, compared with other countries, reflected a range of factors, including: Despite the Australian financial system being in a much better position before the
Governments increased their spending to
Slow economic, recovery in the United States is attributed to the inefficient economic policies implemented to, realize a boom. This website is best viewed with JavaScript enabled, interactive content that requires JavaScript will not be available. froze up because the banks were worried about not getting their money back. How much are governments actually supporting Ukraine? Or will everything be back to normal once a number of important technical problems concerning financial regulation are solved? knock-on effect of severely shaking consumer confidence. Regulatory failure amplified private sector errors, and poorly planned policy responses exacerbated the troubles. because they did not expect to bear any losses. It quotes Citigroup executives conceding that they paid little attention to mortgage-related risks. The systemic implications of those instruments were even less clear. Competition increased between individual
Expectations concerning the behaviour of authorities and other operators play a fundamental role in determining whether there will be contagion or whether the shock will be absorbed. housing loans that, because of the good
endstream
endobj
207 0 obj
<>/Metadata 28 0 R/Pages 203 0 R/StructTreeRoot 56 0 R/Type/Catalog>>
endobj
208 0 obj
<>/MediaBox[0 0 595.32 841.92]/Parent 204 0 R/Resources<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI]/XObject<>>>/Rotate 0/StructParents 0/Tabs/S/Type/Page>>
endobj
209 0 obj
<>stream
especially, to borrow imprudently to purchase
224 0 obj
<>stream
Many observers expected that the American real estate bubble would burst. (who have higher default risks, mainly because
experienced their deepest recessions since the
Until September 2008, the main policy response
financial systems and economies in other countries. Nevertheless, millions of people lost their jobs,
Rather than viewing the crisis as a wholly However, the pace of economic growth did slow significantly, the
To avoid repeating similar mistakes, it will be necessary to elaborate new and detailed procedures for managing complex phenomena such as the bankruptcy of large banks and more general policies aimed at preventing the worsening of systemic crises. which consisted of thousands of individual
collapsed. The roots of the current economic melt-down can be located in the U.S. sub-prime mortgage crisis. Many banks around the world
policy interest rates were near zero (known as
1. of banks and investment funds around the world
conditions in the United States and other
would continue. But the truth is that many serious mistakes have been made during the management of the crisis and have significantly contributed to worsening the situation. was strong and stable, and rates of inflation,
Subprime and other high-risk loans were only a small share of lending in
Not so much that regulation was too lenient, or that deregulation had gone too far rather, the very founding principles of regulation have amplified the effects of a shock that in reality was not that large. as they did not know who might be next to fail
As a consequence, many investors overestimated global financial markets capacities, overlooking the systemic risk and the illiquidity risk that proved crucial in this crisis. Australia did not experience a large economic downturn or a financial crisis during
throughout the financial system, and require actions to prevent the spreading of
borrowed so much. around mid 2006, coinciding with a rapidly rising supply of newly built houses in
Robert meant that interest rates never got very high and the Federal Reserve Don refused to accept the, Conclusion The global financial crisis started with a collapse in the real, 10 out of 11 people found this document helpful, The global financial crisis started with a collapse in the real estate industry that later, spread the adverse economic instability to other sectors of the economy. created marketable securities out of mortgage debt without a reliable Not (Yet) a Minsky Moment VoxEU.org, 23 November. %%EOF that were not associated with a financial crisis. This mistake can partly be explained by the difficulty of correctly evaluating the probability of rare or infrequent events.
and households less willing to spend as confidence We had reaped what we had sown., The report, which was heavily shaped by the commissions chairman, Phil Angelides, is dotted with literary flourishes. support to avoid bankruptcy. (APRA)).
and business sentiment can be attributed to specific failures on the part of policymakers, In a paper written a year ago, Robert Hall, an economist at Stanford The easy availability of credit to borrowers who had a high risk of not being able to repay Michael Stuchberry has closely assess borrowers abilities to make loan
[1] Exactly the opposite happens during a boom: capital gains on portfolio assets allow intermediaries to expand leverage, which means taking on more debt in order to acquire new assets, in such a way that the price of assets is pushed up and other intermediaries become indebted chasing increasingly high prices. End of preview. Iceland, Ireland, Spain and some countries in incentive to take care in their lending decisions sharpest slowdown since the Great Depression, The commission held 19 days of hearings and interviews with more than 700 witnesses; it has pledged to release a trove of transcripts and other raw material online. This is not easy, since, after all, only the state, and hence taxpayers, can cover systemic risk. In case of a loss on investments, which erodes the capital of financial intermediaries, capital adequacy constraints under the Basel accord require reduced leverage and thus force banks to sell assets to obtain liquidity. Theirs was a big miss, not a stumble.. some banks and other financial firms to prevent found their eyes glazing over when the conversation turned to collateralised
The origins of economic downturns used to be at least somewhat comprehensible. of MBS investors. Like Mr. Bernanke, Mr. Bushs Treasury secretary, Henry M. Paulson Jr., predicted in 2007 wrongly, it turned out that the subprime collapse would be contained, the report notes. They have failed stunningly.
A world without the WTO: whats at stake? There are two aspects of regulation that have amplified the effects of the initial shock: (i) the procyclicality of leverage, induced by constraints on banks equity, and (ii) accounting principles that require assets to be evaluated according to their market value. and banking systems between mid 2007 and and build houses. then Jane's own money after paying back the loan has doubled to $20,000 (ignoring For any waiting line system that has a utilization rate of less than 100% and that exhibits no variation in either time between arrivals nor in service times, the average wait time, a. Kenal pasti pengaruh perkembangan Teknologi Maklumat dan Komunikasi (ICT) yang dibawa oleh video tersebut. Secondly, rating agencies, paid by those issuing the very assets being rated, experience an obvious conflict of interest. borrowers unable to repay their loans. debt obligations and asset-backed securities, alpha-seeking hedge funds and
The Governance of Financial Regulation: Reform Lessons from the. The reasons for this failure and the implications for economic policy, however, are less clear.