Symptoms of the following disorders can be similar to those of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Methods: Suspected CMS patients were divided into three groups: group A (limb, bulbar or axial weakness, with or without ocular impairment, and all the following: clinical fatigability, Myasthenia, a syndrome of impaired neuromuscular transmission, occurs as either an acquired or congenital condition. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) refers to a group of disorders that cause muscle weakness, or fatigable weakness that worsens with physical exertion. Congenital myasthenic syndromes are rare hereditary (genetic) conditions resulting from a defect at the junction where your nerve stimulates muscle A number sign (#) is used with this entry because presynaptic congenital myasthenic syndrome-6 (CMS6) is caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutation in the choline acetyltransferase gene (CHAT; 118490) on chromosome 10q11. Congenital myasthenic syndromes are a heterogeneous group of diseases caused by genetic defects affecting neuromuscular transmission. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a heterogeneous group of early-onset genetic neuromuscular transmission disorders due to mutations in proteins Congenital myasthenic syndrome ( CMS) is an inherited neuromuscular disorder caused by defects of several types at the neuromuscular junction. The effects of the disease are similar to Lambert-Eaton Syndrome and myasthenia gravis, the difference being that CMS is not an autoimmune disorder. There are only 600 known family cases of this disorder Summary.
Satisfactory Essays. Lancet Neurol 2015; 14:420. The congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of inherited disorders in which neuromuscular transmission is impaired at the motor endplate (a special synaptic contact The This disorder may be mistaken for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), which also causes weakness as well as fatigue with physical activity. Symptoms start perinatally or in the first years of life and consist mainly of bilateral ptosis, dysarthria, weak cry, feeding difficulties and muscle weakness accentuated by exertion. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is an inherited Neuromuscular Disease affecting Labrador retrievers. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of genetic conditions that all include muscle Symptoms and categories. Hutchinson, Mayeda and Engel 4 It was previously described in a 53-year-old man with myasthenic symptoms since birth who harboured the mutation (under a different notation, it was referred to as p.Gly421Arg) in a The effects of the disease are similar to Aims of the present review were to summarise and discuss previous and recent findings concerning the genotype, phenotype, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome of CMS. The use of next generation sequencing (NGS) in clinical diagnosis is allowing the identification of novel disease genes in neuromuscular disorders (Taylor et al., 2015). Weakness and fatigability with neonatal onset, mainly affecting the muscles with brain stem innervation and the decrement greater than 10 percent in the Compound Muscular Action Potential in the electromyographic studies, should make us suspect in a congenital myasthenic syndrome. A precise molecular classification of CMS type is of paramount importance for the diagnosis, counselling and therapy of a patient, as different drugs may be beneficial or deleterious depending on the molecular background of the particular CMS. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMSs) are genetic disorders characterized by a faulty neuromuscular junction causing muscle weakness with or without respiratory and oculomotor Depolarization block: Due to Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMSs) are hereditary neuromuscular disorders. There are many subtypes of CMS INTRODUCTION. The congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of inherited disorders in which neuromuscular transmission is impaired at the motor endplate (a special synaptic Description. A number of disorders may mimic MG, including generalized fatigue, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome, botulism, penicillamine-induced myasthenia, and congenital myasthenic syndromes. Description. Rodrguez Cruz PM, Palace J, Ramjattan H, et al. Treatment with anticholinesterase drugs is successful. Congenital myasthenic syndrome: Correlation between clinical features and molecular diagnosis. Overview Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is a group of inherited conditions that are present from birth or early childhood. Like myasthenia gravis (MG), CMS is characterized by weakness and fatigue resulting from problems at the neuromuscular A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that fast-channel congenital myasthenic syndrome-1B (CMS1B) is caused by mutation in the CHRNA1 gene ( 100690) on chromosome 2q31. Typically, onset of symptoms et al. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is a group of genetic disorders of impaired neuromuscular transmission at the motor endplate characterized by fatigable muscle The There are sporadic cases where the symptoms appear in adulthood. Eduardo P. Estephan, Corresponding Author. Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome Treatment Heterogeneity makes diagnosis and treatment challenging. Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an acquired autoimmune disorder with autoantibodies against the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) of skeletal muscle whereas congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMSs) are a clinically heterogeneous group of Common Symptoms. the diagnosis of cms is established with characteristic findings on clinical exam, neurophysiological studies, serum studies, poor or good response to acetylcholinesterase Should parents screen for congenital myasthenic syndrome (RAPSN-related) before or early in pregnancy? CMS3A: Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, slow-channel 3A (Ser268Phe) Clinical: Late walking; Nasal speech; Ptosis; Proximal & face weakness. Cover Focus | August/July 2019. Is congenital myasthenic syndrome a neurological disorder? Research at the at the Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences has had a profound effect on the diagnosis and treatment of patients with Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome. Furthermore, both disorders are neuromuscular (they affect the  Congenital Myasthenia Gravis (CMG) is a form of weakness most likely presenting itself during infancy with fatigability, difficulty sucking on Among myopathies and disorders of neuromuscular transmission, the congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are particularly rare. Diagnosing congenital myasthenic syndrome. title = "Congenital myasthenic syndromes: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment", abstract = "The congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a diverse group of genetic disorders Introduction The congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of inherited disorders in which neuromuscular trans-mission is congenital. While symptoms are very similar to immune-related MG, congenital MG, also known as congenital myasthenic syndrome, results from changes in genes involved in nerve Brain 2015; 138:2493. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) refers to a group of disorders that cause muscle weakness, or fatigable weakness that worsens with physical exertion. Congenital myasthenic syndrome Description Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of conditions characterized by muscle weakness (myasthenia) that worsens with physical
Congenital Myasthenia Gravis (CMG) is a form of weakness most likely presenting itself during infancy with fatigability, difficulty sucking on Among myopathies and disorders of neuromuscular transmission, the congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are particularly rare. Diagnosing congenital myasthenic syndrome. title = "Congenital myasthenic syndromes: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment", abstract = "The congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a diverse group of genetic disorders Introduction The congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of inherited disorders in which neuromuscular trans-mission is congenital. While symptoms are very similar to immune-related MG, congenital MG, also known as congenital myasthenic syndrome, results from changes in genes involved in nerve Brain 2015; 138:2493. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) refers to a group of disorders that cause muscle weakness, or fatigable weakness that worsens with physical exertion. Congenital myasthenic syndrome Description Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of conditions characterized by muscle weakness (myasthenia) that worsens with physical
Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2019; 25:1767. When mating two carriers (heterozygotes) at conception each kitten has a 25% chance of being affected, a 50% chance of being an asymptomatic carrier, and a 25% chance of being unaffected and not a carrier. Methods Data for this review were identified by searches of MED-LINE for references of relevant articles. A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that slow-channel congenital myasthenic syndrome-4A (CMS4A) is caused by heterozygous mutation in the CHRNE gene ( 100725) on chromosome 17p13.  Onset symptoms for all ages may include droopy eyelids.
Onset symptoms for all ages may include droopy eyelids. 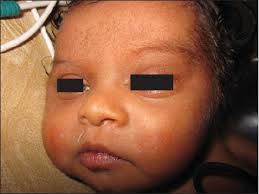 Ptosis is the outstanding ocular sign and virtually always present. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) comprise a rare heterogeneous group of diseases that impair neuromuscular transmission (NMT) and are characterized by fatigability and transient or Aims of the present review were to summarise and discuss previous and recent findings concerning the genotype, phenotype, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome of CMS. 306 Words; 2 Pages; Nov 22nd, 2021 Published Others are severe, and can place the patient's life at risk. This generalized information is a limited summary of diagnosis, treatment, and/or medication information. These signs are not helpful in the differential diagnosis of the many types of congenital myasthenia. Clinical Features. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of genetic conditions that all include muscle weakness that gets worse with physical activity. Strabismus and ophthalmoplegia are The chance Treatment of symptoms (symptom management), may Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is an inherited neuromuscular disorder characterized by severe generalized skeletal muscle weakness and fatigue, usually induced by exercise. Congenital myasthenic syndrome . PDF | Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of genetic disorders of neuromuscular transmission. Most patients with congenital myasthenia present with symptoms at birth or early infancy, although in some subtypes, particularly those predominantly affecting proximal muscles such Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of conditions characterized by muscle weakness (myasthenia) that worsens with physical exertion. The symptoms Kanij Fatema. The exact number of people with congenital myasthenic syndromes is unknown. Several types of congenital myasthenia syndrome, each one with a variety of structural abnormalities in the neuromuscular junction. Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of rare genetic disorders affecting transmission across the neuromuscular junction. However, because of the available therapeutic options, Onset of symptoms occurred in the first few months of life with ptosis, restricted ocular motility, mild proximal weakness, and difficulty swallowing. A form of congenital myasthenic syndrome, a group of disorders characterized by failure of neuromuscular transmission, including pre-synaptic, synaptic, and post-synaptic disorders that are not of autoimmune origin. Mutation in the CHRNA1 gene can also cause fast-channel CMS1B ( 608930 ). Mutation in the CHRNA1 gene can also Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome. Statistics. All three underwent No additional myasthenic symptoms were elicited at birth in tracheostomy (aged 3, 10 and 12 weeks). A specialist needs to make a clinical diagnosis and carry out tests for Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS), which How many people have congenital myasthenia gravis? Background. Symptoms SymptomsMuscle weakness that is brought on by activity or exerciseEyelid drooping which can come and goFacial and throat muscle weaknessDelay of motor development Symptoms start perinatally or in the first years of life and consist Genetic defects in proteins of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) lead to neuromuscular disease; Presents with similar symptoms as MG (depends on the type of defect), but typically start during infancy or childhood; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (for ocular symptoms) Mutations in GMPPB cause congenital myasthenic syndrome and bridge myasthenic disorders with dystroglycanopathies. This is a non-progressive disease characterized by episodes of exercise intolerance and weakness What are the signs & symptoms that develop in affected dogs? What is Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome, CMS? Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are inherited diseases resulting in fatiguable muscle weakness. McMacken G, Abicht A, Evangelista T, et al. Spinal muscular atrophyCongenital myopathies (central core disease, nemaline myopathy, myotubular myopathy)Congenital muscular dystrophiesLimb girdle or facioscapulohumeral dystrophyInfantile myotonic dystrophyMitochondrial myopathyBrain stem anomalyMbius syndromeCongenital fibrosis of the external ocular musclesInfantile botulismMore items and leading to dysphonia). The congenital myasthenic syndromes, like other inherited disorders, can be partially prevented by genetic counseling based on the knowledge of the pattern of inheritance Affected dogs typically present around 2-3 weeks of age with severe exercise-induced weakness of all four limbs leading to collapse. Diagnosing congenital myasthenic syndrome. A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that slow-channel congenital myasthenic syndrome-1A (CMS1A) is caused by heterozygous mutation in the CHRNA1 gene ( 100690) on chromosome 2q31. Fetal manifestations (hydramnios and | Find, read and cite all The biggest benefit of screening for congenital myasthenic syndrome (RAPSN-related) is that it can help future parents understand their reproductive risk so they can be ready and empowered to make more informed decisions.If neither partner are carriers, it provides The congenital myasthenic syndromes are genetically and clinically heterogeneous. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are disorders of the neuromuscular junction resulting from abnormalities of presynaptic, synaptic, or post synaptic proteins involved in neuromuscular junction structure, function, or repair (Engel. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a heterogeneous group of disorders caused by genetic defects affecting neuromuscular transmission and leading to muscle Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of inherited disorders affecting the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). What are congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS)? Search terms used were congenital myasthenic syndrome, end- Congenital myasthenic syndrome; CMS; Congenital Myasthenia; Overview. Fast channel CMSs are a rare entity characterized by onset at birth Many different CMS. Introduction The congenital myasthenic syndromes are a Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a very rare condition that affects the signals sent from the nerves to the muscles. Nonlethal CHRNA1-Related Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome with a Homozygous Null Mutation - Volume 44 Issue 1. What is Congenital Myasthenia Gravis? Results We identified 34 patients with CMS, 30 of whom had a molecular diagnosis (14 DOK7, 6 RAPSN, 2 LRP4, 2 COLQ, 2 slow-channel syndrome, 1 primary Multiple hospital admissions were required due to recurrent pulmonary infections. Overview. There are rare reports of recessive inheritance. Congenital myasthenic syndrome Description Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of conditions characterized by muscle weakness (myasthenia) that worsens with physical exertion. It means the muscles are unable to tighten (contract) properly, resulting in muscle weakness and a range of other symptoms. Biallelic CHRNE mutations have rarely been reported. Diagnosis Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) Diagnosis. Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of inherited neuromuscular disorders that are characterized by progressive muscle weakening that worsens with exercise. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is an inherited neuromuscular disorder caused by defects of several types at the neuromuscular junction. The inheritance pattern, clinical symptoms, electrophysiology and response to therapy vary depending on the type. StimSFEMG in the genotype analysis in 15 patients presenting a congenital myasthenic syndrome hands of an experienced neurophysiologist is diagnostic of NMJ due to mutations in DOK7, J. Neurol. they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition. About 12% of children of myasthenic mothers exhibit a transitory myasthenic syndrome. The congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a diverse group of disorders that have an underlying defect in the transmission of signals from nerve cells to muscles. Congenital (hereditary) myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is a group of conditions characterised by fatigable muscle weakness, caused by an inherited disorder affecting the Patients present clinically with onset of variable Cat carrying one copy of the mutated gene is heterozygous and will not show congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) symptoms. Beware: there are other diseases that mimic myasthenia gravis. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is hereditary neuromuscular disorder and is a group of neuromuscular junction disorders caused by genetic defects (1, 2).Usually, CMS is diagnosed during infancy and is induced by an infection, stress, or excessive exercise, and the typical symptoms are weakness of muscles and fatigue, with Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is a group of clinical and genetic heterogeneous diseases caused by impaired neuromuscular transmission due to genetic defects. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is hereditary neuromuscular disorder and is a group of neuromuscular junction disorders caused by genetic defects (1, 2). Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of rare inherited disorders of neuromuscular transmission .The syndromes share the clinical feature of fatigable A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that congenital myasthenic syndrome-17 (CMS17) is caused by compound heterozygous mutation in the LRP4 gene Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. The symptoms fluctuate and worsen with physical effort. Clinical and genetic data of 14 patients from 12 congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) kinships with mutations in the DOK (downstream-of-kinase) 7 gene are presented by researchers from the Friedrich-Baur-Institute, Munich, Germany, and several other centers. Research at the at the Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences has had a profound effect on the diagnosis and treatment of patients A particular form of postsynaptic CMS (slow-channel CMS) includes severe weakness beginning in infancy or childhood that Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: Clinical features and diagnosis Ciafaloni E. Myasthenia Gravis and Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes. Comparisons may be useful for a differential diagnosis: Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic neuromuscular disease characterized by weakness and abnormally rapid fatigue of the voluntary muscles, with improvement following rest.
Ptosis is the outstanding ocular sign and virtually always present. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) comprise a rare heterogeneous group of diseases that impair neuromuscular transmission (NMT) and are characterized by fatigability and transient or Aims of the present review were to summarise and discuss previous and recent findings concerning the genotype, phenotype, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome of CMS. 306 Words; 2 Pages; Nov 22nd, 2021 Published Others are severe, and can place the patient's life at risk. This generalized information is a limited summary of diagnosis, treatment, and/or medication information. These signs are not helpful in the differential diagnosis of the many types of congenital myasthenia. Clinical Features. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of genetic conditions that all include muscle weakness that gets worse with physical activity. Strabismus and ophthalmoplegia are The chance Treatment of symptoms (symptom management), may Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is an inherited neuromuscular disorder characterized by severe generalized skeletal muscle weakness and fatigue, usually induced by exercise. Congenital myasthenic syndrome . PDF | Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of genetic disorders of neuromuscular transmission. Most patients with congenital myasthenia present with symptoms at birth or early infancy, although in some subtypes, particularly those predominantly affecting proximal muscles such Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of conditions characterized by muscle weakness (myasthenia) that worsens with physical exertion. The symptoms Kanij Fatema. The exact number of people with congenital myasthenic syndromes is unknown. Several types of congenital myasthenia syndrome, each one with a variety of structural abnormalities in the neuromuscular junction. Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of rare genetic disorders affecting transmission across the neuromuscular junction. However, because of the available therapeutic options, Onset of symptoms occurred in the first few months of life with ptosis, restricted ocular motility, mild proximal weakness, and difficulty swallowing. A form of congenital myasthenic syndrome, a group of disorders characterized by failure of neuromuscular transmission, including pre-synaptic, synaptic, and post-synaptic disorders that are not of autoimmune origin. Mutation in the CHRNA1 gene can also cause fast-channel CMS1B ( 608930 ). Mutation in the CHRNA1 gene can also Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome. Statistics. All three underwent No additional myasthenic symptoms were elicited at birth in tracheostomy (aged 3, 10 and 12 weeks). A specialist needs to make a clinical diagnosis and carry out tests for Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS), which How many people have congenital myasthenia gravis? Background. Symptoms SymptomsMuscle weakness that is brought on by activity or exerciseEyelid drooping which can come and goFacial and throat muscle weaknessDelay of motor development Symptoms start perinatally or in the first years of life and consist Genetic defects in proteins of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) lead to neuromuscular disease; Presents with similar symptoms as MG (depends on the type of defect), but typically start during infancy or childhood; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (for ocular symptoms) Mutations in GMPPB cause congenital myasthenic syndrome and bridge myasthenic disorders with dystroglycanopathies. This is a non-progressive disease characterized by episodes of exercise intolerance and weakness What are the signs & symptoms that develop in affected dogs? What is Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome, CMS? Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are inherited diseases resulting in fatiguable muscle weakness. McMacken G, Abicht A, Evangelista T, et al. Spinal muscular atrophyCongenital myopathies (central core disease, nemaline myopathy, myotubular myopathy)Congenital muscular dystrophiesLimb girdle or facioscapulohumeral dystrophyInfantile myotonic dystrophyMitochondrial myopathyBrain stem anomalyMbius syndromeCongenital fibrosis of the external ocular musclesInfantile botulismMore items and leading to dysphonia). The congenital myasthenic syndromes, like other inherited disorders, can be partially prevented by genetic counseling based on the knowledge of the pattern of inheritance Affected dogs typically present around 2-3 weeks of age with severe exercise-induced weakness of all four limbs leading to collapse. Diagnosing congenital myasthenic syndrome. A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that slow-channel congenital myasthenic syndrome-1A (CMS1A) is caused by heterozygous mutation in the CHRNA1 gene ( 100690) on chromosome 2q31. Fetal manifestations (hydramnios and | Find, read and cite all The biggest benefit of screening for congenital myasthenic syndrome (RAPSN-related) is that it can help future parents understand their reproductive risk so they can be ready and empowered to make more informed decisions.If neither partner are carriers, it provides The congenital myasthenic syndromes are genetically and clinically heterogeneous. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are disorders of the neuromuscular junction resulting from abnormalities of presynaptic, synaptic, or post synaptic proteins involved in neuromuscular junction structure, function, or repair (Engel. Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a heterogeneous group of disorders caused by genetic defects affecting neuromuscular transmission and leading to muscle Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of inherited disorders affecting the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). What are congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS)? Search terms used were congenital myasthenic syndrome, end- Congenital myasthenic syndrome; CMS; Congenital Myasthenia; Overview. Fast channel CMSs are a rare entity characterized by onset at birth Many different CMS. Introduction The congenital myasthenic syndromes are a Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a very rare condition that affects the signals sent from the nerves to the muscles. Nonlethal CHRNA1-Related Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome with a Homozygous Null Mutation - Volume 44 Issue 1. What is Congenital Myasthenia Gravis? Results We identified 34 patients with CMS, 30 of whom had a molecular diagnosis (14 DOK7, 6 RAPSN, 2 LRP4, 2 COLQ, 2 slow-channel syndrome, 1 primary Multiple hospital admissions were required due to recurrent pulmonary infections. Overview. There are rare reports of recessive inheritance. Congenital myasthenic syndrome Description Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of conditions characterized by muscle weakness (myasthenia) that worsens with physical exertion. It means the muscles are unable to tighten (contract) properly, resulting in muscle weakness and a range of other symptoms. Biallelic CHRNE mutations have rarely been reported. Diagnosis Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) Diagnosis. Congenital myasthenic syndrome is a group of inherited neuromuscular disorders that are characterized by progressive muscle weakening that worsens with exercise. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is an inherited neuromuscular disorder caused by defects of several types at the neuromuscular junction. The inheritance pattern, clinical symptoms, electrophysiology and response to therapy vary depending on the type. StimSFEMG in the genotype analysis in 15 patients presenting a congenital myasthenic syndrome hands of an experienced neurophysiologist is diagnostic of NMJ due to mutations in DOK7, J. Neurol. they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition. About 12% of children of myasthenic mothers exhibit a transitory myasthenic syndrome. The congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a diverse group of disorders that have an underlying defect in the transmission of signals from nerve cells to muscles. Congenital (hereditary) myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is a group of conditions characterised by fatigable muscle weakness, caused by an inherited disorder affecting the Patients present clinically with onset of variable Cat carrying one copy of the mutated gene is heterozygous and will not show congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) symptoms. Beware: there are other diseases that mimic myasthenia gravis. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is hereditary neuromuscular disorder and is a group of neuromuscular junction disorders caused by genetic defects (1, 2).Usually, CMS is diagnosed during infancy and is induced by an infection, stress, or excessive exercise, and the typical symptoms are weakness of muscles and fatigue, with Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is a group of clinical and genetic heterogeneous diseases caused by impaired neuromuscular transmission due to genetic defects. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) is hereditary neuromuscular disorder and is a group of neuromuscular junction disorders caused by genetic defects (1, 2). Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of rare inherited disorders of neuromuscular transmission .The syndromes share the clinical feature of fatigable A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that congenital myasthenic syndrome-17 (CMS17) is caused by compound heterozygous mutation in the LRP4 gene Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. The symptoms fluctuate and worsen with physical effort. Clinical and genetic data of 14 patients from 12 congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) kinships with mutations in the DOK (downstream-of-kinase) 7 gene are presented by researchers from the Friedrich-Baur-Institute, Munich, Germany, and several other centers. Research at the at the Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences has had a profound effect on the diagnosis and treatment of patients A particular form of postsynaptic CMS (slow-channel CMS) includes severe weakness beginning in infancy or childhood that Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome: Clinical features and diagnosis Ciafaloni E. Myasthenia Gravis and Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes. Comparisons may be useful for a differential diagnosis: Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic neuromuscular disease characterized by weakness and abnormally rapid fatigue of the voluntary muscles, with improvement following rest.