UNDP hosts flagship events and co-hosts a multitude of events at the HLPF, together with Member State, UN and other partners. UNDP's new Strategic Plan is based on the principles of "leaving no one behind" and "reaching the furthest behind first". endobj We do this by integrating our network and array of disciplines with the skills of our humanitarian, development and peacebuilding partners from conflict prevention, risk management and pandemic preparedness to climate security, early warning systems and green recovery. UNDP also plays a leading role in supporting the secretariat of the International Aid Transparency Initiative (IATI). The SDG Philanthropy Platform is a global partnership initiative between UNDP and Rockefeller Philanthropy Advisers designed to help philanthropy from around the world understand better the opportunities for engaging in the SDGs, and their responsibilities as they engage; help governments and the UN system understand the added value of philanthropy's engagement; develop large scale collaborations which shift systems towards sustainable development results. The CSAC currently functions as the main institutional mechanism for dialogue between civil society leaders and UNDP senior management.
At the 2018 session of the HLPF, UNDP convened a corporate side event on Nature for Life: Accelerating SDGs Progress by Investing in People and Planet. One of UNDP's key functions lies in convening a wide variety of partners at international, regional, national and subnational levels to help facilitate exchanges of experience, peer and mutual learning. 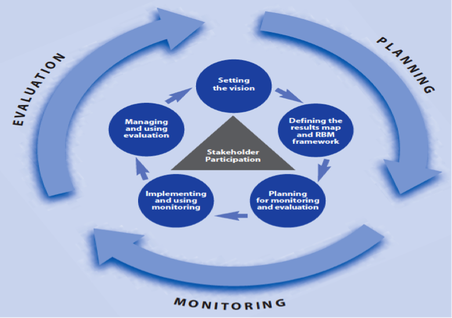
Its contents are the sole responsibility of UNDP-UNEP Poverty-Environment Action for Sustainable Development Goals and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Governments of Austria, Belgium, Norway, Sweden or the European Union. These services are accessed at the request of host governments, or at request of other agencies where agencies have no presence. <>/ExtGState<>/XObject<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 R/Group<>/Tabs/S/StructParents 0>> In partnership with UNECA, IDRC and World Wide Web Foundation, UNDP produced the 2018 Africa Data Revolution Report, which assesses the current state of open government on the continent and identifies areas where open data provides the greatest returns on investment in Africa.
To deliver on its mandate as "integrator" of sustainable development, UNDP has reconfigured its policy capacity into a worldwide Global Policy Network which, in combination with our Accelerator Labs, scale up UNDPs capacity to mobilize multi-disciplinary expertise to help UNCTs and Governments design and implement innovative integrated solutions to respond to complex development challenges and accelerate SDG progress. Country reporting is critical not only for tracking national progress, but also in providing baselines and more regular progress overviews to inform national SDG implementation and monitoring. This approach is both core to UNDPs work and key part of UNDPs Next Generation improved business model. Our modus operandi is the leveraging of interlinkages across SDG goals and targets - more specifics in the individual entries above and below. The previous Strategic Plan (2014-2017), while articulated before the adoption of the 2030 Agenda, was developed drawing on a strong sustainable development vision, incorporating many of the principles underlying the 2030 Agenda. Following the reform of the UN Development System, the standard operating procedures for MAPS have been revised in consultation with sister agencies in the UNSDG Task Team 1 on Integrated Policy Support (Strategic Results Group on SDGs), in order to strengthen inter-agency ownership of the MAPS process, and enhance synergies with the Common Country Assessment and UN Sustainable Development Cooperation Framework processes. - A series of signature solutions that define the core work of UNDP; Results Oriented Annual Reports (ROARs) add qualitative evidence to monitor the organisation's support to the implementation of the 2030 Agenda. UNDP collaborated with OHCHR, UNICEF, UN Women, UNFPA, UNHCR and WHO to develop the UNSDG Operational Guide to UNCTs on Leaving No One Behind (LNOB). The Global Festival of Action for Sustainable Development aims to celebrate, empower, and connect the global community driving action for the SDGs. In some cases, UNDP is the service provider of last resort and often a key asset in settings of fragility. UNDP actively contributes to the series of VNR Knowledge Exchange seminars convened by UNDESA. It offers a framework to identify, track and prioritize the furthest behind; better understand and address the spectrum of deprivations and disadvantages that leave people behind across the SDGs. vOm}ST-A5_U~z pA. UNDP has established the "Financing Solutions for Sustainable Development" Platform that provides guidance to policy makers and researchers in selecting, reviewing and operationalising financing solutions to fund SDG-aligned national and sectoral development plans. It is organised by the UN SDG Action Campaign (which is hosted by UNDP) with the support of the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development and the German Federal Foreign Office. pb.=I$(. Taking place in Bonn each year, the Global Festival of Action for Sustainable Development provides a dynamic and interactive space to showcase the latest innovations, tools and approaches to SDG implementation. J.nX}Z$>~$7d_ZSw>s-@^CDEbq(gr7/6VOz[4!n*jI74)$jl,9iEYXb5j0 _ G+% 3) UNDP provides a unique service to the UN development system as the backbone of the system at country-level, and convener of partnerships. These tools notably include the Human Development Index and the Multidimensional Poverty Index, the Climate, Land-Use, Energy and Water Systems (CLEWS) integrated modelling framework in collaboration with UNDESA and the Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden; the International Futures forecasting and scenario analysis tool with University of Denver; the iSDG modelling tool with Millennium Institute. Recognising that civil society actors often serve as both a driving force in guiding development policies and as a watchdog to make sure policies get implemented, UNDP facilitates civil society participation in all facets of implementing the 2030 Agenda. Leaving no one behind is hard to visualize in so many contexts today. BCtA member companies are market leaders that provide examples of successful, profitable and scalable models for reaching poor communities and contributing to global development. r 2`1&Cf0jp`e}6 5%>iR.kXc>@FN! ~>(QVIL>EDAsdl,c9H3F[ 0='}VL lZXpQ?-wsi&/7_TzV% In an effort to reinforce the principle to leave no one behind in its own operations, UNDP has introduced an LNOB marker, a unique way to monitor and track its investment in particular groups that are often left behind including: people with disabilities; migrants; etc. UNDP Digital Strategy: https://digitalstrategy.undp.org/. 4 0 obj Meanwhile, the world is experiencing mega-trends which can affect prospects for achieving the SDGs. Department of Economic and Social Affairs, High-level Political Forum on Sustainable Development, UN Conferences and High-Level Events related to sustainable development, Multi-stakeholder Forum on Science, Technology and Innovation for the SDGs, Second Committee of the UN General Assembly , Multidimensional Vulnerability Index for SIDS, the "Financing Solutions for Sustainable Development" Platform, http://www.iicpsd.undp.org/content/istanbul/en/home/. %PDF-1.7 Link to UNDP annual report: https://annualreport.undp.org/. Responding to requests from Member States for coherent and integrated support from the UN development system in implementing the 2030 Agenda, UNDP spearheaded the development of the Mainstreaming, Acceleration, Policy Support (MAPS) common approach, which was formally adopted by the UNDG in October 2015. It should foster a national conversation that can inform policies and concrete action. Its core objectives are to provide practical methods and campaigns for direct people's engagement in SDG implementation; encourage public ownership of SDGs through innovative communications, campaigning and policy advocacy; sponsor people-driven processes to monitor SDG progress through generation/collection of data, evidence, and sentiment about the impact of the SDGs, using the results for local advocacy. BCtA is a unique multilateral alliance among donor governments - including the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida), the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation, the UK Department for International Development (DFID), the US Agency for International Development (USAID), and the United Nations Development Programme, which hosts the secretariat. The Accelerator Labs work with entrepreneurs, engineers, data scientists and grassroots innovators across 78 countries and territories to source locally-driven innovations and scale them to acceleration progress on the SDGs. The Strategic Plan sets out a vision for the evolution of UNDP over the next four years, responding to a changing development landscape and the evolving needs of our partners. % \lDI*%VGJU_~e.$$72v}]^"8l UNDP worked closely with the Chinese Presidency of the G20 in 2016 to adopt a G20 2030 Action Plan for Sustainable Development, which was endorsed by G20 Leaders at the Hangzhou Summit. In accordance with UN programming principles, it is underpinned by human rights, gender equality and women empowerment; sustainability and resilience; and accountability. UNDP supports the inter-governmental process on the SDG Indicators, including the development and implementation of indicators on multi-dimensional poverty (SDG1), the effectiveness, quality and representativeness of public service, access to justice (SDG16) and development cooperation (SDG17). With nine out of our ten largest programmes in fragile or crisis-affected countries and a new Crisis Bureau in place, we are intensifying efforts to reach those who need support the most. These tools notably include the Human Development Index and the Multidimensional Poverty Index, the Climate, Land-Use, Energy and Water Systems (CLEWS) integrated modelling framework in collaboration with UNDESA and the Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden; the International Futures forecasting and scenario analysis tool with University of Denver; the iSDG modelling tool with Millennium Institute. Along with DCO, and in liaison with partners in the UN Development System, UNDP has co-led the development of an executive-level foundational training course on the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (SDG Primer), which provides Resident Coordinators a common base of understanding and approach for the UN system in supporting the 2030 Agenda. UNDP and the French Development Agency (AFD) also prepared a joint report that looks at how the Least Developed Countries can make better use of a more diverse financing for development 'tool-box' ("Financing the SDGs in the Least Developed Countries (LDCs): Diversifying the Financing Tool-box and Managing Vulnerability" 2016). In 2018-2019, UNDP has actively supporting VNR formulation in 35 countries, facilitating multi-stakeholder consultations in preparation of their reports, but also for follow-up on the VNRs. UNDP's contributes substantively to the annual ECOSOC Financing for Development Forums as well to the work of the Inter-Agency Task Force on FfD (IATF), which is mandated to report on progress in implementing the FfD outcomes and the means of implementation of the 2030 Agenda through its annual reports. They involve teams of global and regional experts working closely with UN Country Teams to provide tailored advice and to help foster high-level national ownership of the SDGs as well as stakeholder engagement, taking a comprehensive, integrated approach across multi-dimensional issues. Our goal must be a 21st century UN development system that is more focused on people, less on process; more on results for the poor and marginalised, less on bureaucracy; more on providing integrated support across familiar silos, less on turf battles and competition. Through our growing global partnerships across all sectors, and as part of a strong, capable UN system, we can build on lessons learned; to overcome the biggest challenges as we reach Agenda 2030 and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). UNDP hosts the UN SDG Action Campaign that supports the UN system and Member States on awareness-raising, generating political will, empowering and inspiring people across the world to act on the SDGs. N-I The organisation's policy expertise was brought to bear on the process through substantive focal points on 15 out of 17 SDGs. The global platform connects to country activities in Kenya, Colombia, Ghana, Indonesia and Zambia, India, Brazil. The Handbook was accompanied with an online course providing practical guidance and training to policymakers, statisticians, practitioners and others seeking or engaged in developing a national Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI). UNDP has extensive presence on the ground with staff working in nearly 170 countries and territories; long-standing and trusted relationships with governments and other partners; and a unique ability to develop and help implement the multi-sectoral and integrated development solutions that are needed today - not least by being able to work with and through partnership with stakeholder groups of every kind. 3 0 obj 4) It provides a significant volume of services because local conditions demand it. It also sets out modes for strengthening G20 coherence and coordination on sustainable development. UNDP produced this on behalf of the UNDG. UNDP supports countries in implementing the 2030 Agenda through a mix of policy advisory, technical assistance, capacity building, financing and programme implementation modalities. endobj Over 200 companies, ranging from multinationals to social enterprises, and working in 67 countries, have already responded to BCtA by committing to improve the lives and livelihoods of millions in developing countries through access to markets, financial services, affordable healthcare, water and sanitation, education and other critical services. >~^~m8[T T xJSyxJg! It is therefore critical that the UN system respond with high-quality policy and programme responses, tailored to country-specific realities, and conducive to achieving the SDGs. To help implement the pledge, UNDP works with countries to deepen local understanding of who and why people are - or are at risk of - being left behind; shape according policies; strengthen mechanisms that facilitate their voice and participation; and to track and report on relative progress within the context of national SDG monitoring. Through the Facility for the SDG Implementation in fragile contexts, UNDP supported VNR processes in five g7+ countries in 2019. Through our bold Strategic Plan 2022-2025, we are dialing up our ambition to become the worlds most valuable development partner. UNDP has supported the process of developing indicators for the SDGs throughout the inter-governmental process since its inception, and contributes as observer to the work of the Inter-Agency and Expert Group on SDG Indicators. 1 0 obj UNDP published a handbook on "How to Build a National Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): Using the MPI to inform the SDGs", jointly produced with the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) at University of Oxford. Additionally, UNDP acted as coordinator of inter-agency coalitions such as UN-Water, or as convenor and facilitator mobilising a broad range of expertise, such as the Global Alliance for Monitoring SDG 16. :,%;tEU`+D`(z5t@>~x Strong and broad-based partnerships become ever more important for SDG achievement. On 28 November 2017, UNDP's Executive Board endorsed the new Strategic Plan (2018-2021) that is anchored in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and committed to the principles of universality, equality and leaving no one behind. All rights reserved. Business Call to Action: https://www.businesscalltoaction.org/. (Please see entries to other questions for specifics on cooperation with entities across the UN system.). The UNDP Administrator is the Vice-Chair of the UN Sustainable Development Group; and Co-Chair (with the USG of OCHA) of the Joint Steering Committee for development and humanitarian coordination. (k,e7gH6tz9cF)9(-Jb~po;6Cqj`zKPn9+z,3%Q^i,;=B#0 I>&}9A#7 These are extraordinary times and UNDP is rising to the challenge. Every year, we organise or co-organise a multitude of such events, including in the context of the High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development and other key SDG-related fora. C)D+Dg"ySI Fif Y A0i,&D?_]N:vD8Y)sa&l4A ( 5,o\]LK]b$v=_&atdys3U' p5xQXd((`L1u(!-R (0MCS1K?7k[~?c?c UNDP's Strategic Plan (2018-2021) was developed in close cooperation with UNFPA, UNICEF and UNWOMEN that all prepared their strategic plans following the same planning cycle. UNDP's role can be outlined in four broad aspects: 1) It has deep expertise/specialisation in some specific areas where it can demonstrate competencies across a development topic, and the related SDG targets as areas of concentration; In 2019, our investment in resilience included fostering regional stability in the Sahel, helping Mozambique recover from Cyclone Idai, and supporting over 850,000 refugees and host communities across five countries in response to the Syrian crisis. Emv#a>?WF`QXQ[>s;PgbkApU~p~X15^v{RAS3m N+gXSy?L5Hwiga DYh3 T 8tK'M(]r/Oe|{AZ0 With UNICEF, UNFPA and UN-Women, UNDP has also identified common SDG targets/indicators to monitor common areas of work. In close collaboration with partners in the UN system, think tanks and academia, UNDP deploys and strengthens country capacities to rollout integrated analytical tools and approaches as part of its service offer on SDG integration and its support to MAPS engagements. We are engaging with foundations in country based dialogues about the implementation of the 2030 Agenda. A Joint MAPS team has been established, hosted by UNDP and with dedicated capacity from UNDP and UNICEF, to support the UNSDG Task Team 1 in its oversight of MAPS Engagements. The follow up and review (FuR) process of the 2030 Agenda and SDGs includes mutually reinforcing processes at different levels. Among other things, this resulted in a strengthening of the civic engagement dimension of UNDP's policies and programmes, as well as in greater collaboration between UNDP and a broad range of civil society constituencies. UNDP works with companies from a variety of sectors, for example, water, energy, extractives, food and agriculture, consumer products, healthcare, finance and information technology. Focusing on SDG 16 as an enabling goal of Agenda 2030 and through the application of SDG 16 principles of inclusivity, accountability and participation, is developing an offer to provide deeper support on reporting on SDG 16 especially in fragile contexts and enhance follow-up action after the reporting. Global Festival of Action for Sustainable Development: http://globalfestivalofaction.org/. Leaving no one behind is at the core of UNDP's programming. It also is trusted as a scorekeeper on development goals, and as a provider of institutional capacity development services in support of the 2030 Agenda at large. <> UNDP supports policymaking, implementation and mainstreaming of the SDGs in fragile and conflict affected situations. To help illustrate this goal, we are pleased to share with you our UNDP Strategic Plan 2022-2025 Microsite (in French and Spanish) which outlines how UNDP aims to create greater impact and results over the next four years and beyond. Its successor initiative, MY World 2030, aims to collect globally comparable data on how people feel their lives are changing to support efforts to report on progress on the SDGs. Lw`g5)r$BM& |STK6d'Vwm\v;nIHv18 ,jz|miX T2T UNDP's partnership with civil society actors spans multiple domains, including programme implementation, policy development and advocacy. These tools help understand why and how investing in certain policy priorities is more likely to move the needle for the achievement of SDGs than others, and to advise policymakers on SDG solutions that are more likely to achieve lasting development impact. stream Adopting a truly integrated approach presents complex challenges. The Digital Strategy describes how UNDP will transform, framed through two inter-related transformation pathways: Digital Transformation Pathway 1 looks outward at how we can use digital technologies to improve the way we work, including how we deliver, create, collaborate and advocate.
The UNDP Civil Society Advisory Committee (CSAC) was established in 2000 to systematise the consultation process between UNDP and civil society actors at the global level. The strategic goal of UN/UNDP's engagement with the G20 is to align G20 policy actions with the UN Agenda, and to use its weight and political clout to address global challenges and make sustainable development an overarching guiding principle of its macro policy framework. UNDP formulates a medium-term strategic plan every four years, which allows for adapting UNDP's services to evolving circumstances. The G20 Action Plan reflects the comprehensiveness and universality of the 2030 Agenda by focusing on G20 collective actions and including the contribution of the entire G20 agenda and all work streams towards the SDGs. In application of the UN Sustainable Development Group's Mainstreaming, Acceleration and Policy Support (MAPS) approach, UNDP works with sister agencies in the UNSDG to deploy integrated policy support missions to support countries in mainstreaming the SDGs into national plans, policies, and institutional mechanisms, so-called 'MAPS missions and engagements'. We believe that this approach will help us to deliver what we do best: integrated development solutions driven by country priorities. In 2019, UNDP established the SDG Finance Sector Hub to bring coherence and scale to its work on financing for the Sustainable Development Goals, with a range of services to support public and private partners in figuring out how to shift from funding to financing Agenda 2030. For example: UNDP has taken a lead role in line with its mandate, and in close collaboration with colleagues and partners inside the UN system and beyond, on implementing, monitoring, and reporting on peaceful, just and inclusive societies, and the catalysing role of SDG across the entire 2030 Agenda. The Guide presents as its first analytical entry point, the five-factor framework developed by UNDP that suggests the need to consider and tackle the multiple and intersecting dimensions that conspire to leave people behind (identity/discrimination, socio-economic standing, geography, governance, vulnerability to shocks and crises). In some countries, MAPS engagements have also helped to begin operationalizing humanitarian-peace-development linkages. (Y?"*JidZri-S`60b|IzjW'XJl0
UNDP's collaboration with the private sector takes various forms: The Istanbul International Center for Private Sector in Development (IICPSD) supports the private sector and foundations to become transformative partners in development through research, advocacy for inclusive business, facilitation of public-private dialogue and brokering partnerships. It facilitated the drafting process, including coordinating contributions by G20 members and international organisations. The event was a platform to demonstrate how investing in natural resource management accelerates SDG progress on livelihoods, jobs, women and youth empowerment, growth, climate change, migration, peace and stability; and highlight the links between natural resource governance, sustainable and resilient societies, and efforts to achieve the SDGs. Rapid Integrated Assessment to gauge the level of alignment between a country's national plan and the SDG targets; Institutional Context Analysis to better understand a country's political economy; Bottleneck Analysis to consider sector-specific and cross-cutting impediments to progress; PovRisk tool to identify the determinants that lead to people sliding back into poverty; Modelling and micro-simulation tools (in collaboration with UN-DESA) that allow policymakers to assess interlinkages between SDG goals and targets; SDG-specific forecasting tool (in collaboration with University of Denver) to support SDG acceleration efforts. endobj
UNDP takes an active role in all relevant coordination systemwide mechanisms. In close collaboration with partners in the UN system, think tanks and academia, UNDP is deploys and strengthens country capacities to rollout integrated analytical tools and approaches as part of its service offer on SDG integration and its support to MAPS engagements. As you will see, the heart of our development offer is a clear 3x6x3 framework, combining 3 directions of change, 6 signature solutions and 3 enablers. <>/Metadata 723 0 R/ViewerPreferences 724 0 R>> It emphasizes that, across all the contexts in which it works, UNDP will prioritise the collection and use of disaggregated data and analyses for identifying those being left behind, and support the design of targeted interventions to reach them. In parallel, UNDP is also collaborating with UNICEF to develop a companion technical training package intended to equip UN staff and country partners with practical approaches, tools and methods to be able to support and participate in MAPS engagements more coherently and consistently. j8`9Aov@ a{$ % This service offer on SDG Integration focuses not on individual SDGs, but on the gaps between them the missing pieces that make the 2030 Agenda whole. UNDPs new policy support architecture, the Global Policy Network, is anchored by a service offer on SDG Integration consisting of four dedicated streams of work to support countries in their efforts to design policy and programmes for the future, access and generate finance, source and analyze data, and drive innovation and learning. Knowledge and information sharing platform containing a set of tools at www.LocalizingTheSDGs.org. Due to its large global presence, even in areas where it is not thematically a lead agency, its project management and execution capabilities are available. Launch of UNDP Strategic Plan 2022-2025 Microsite, 25 October. UNDP partners with a broad range of formal and informal civil society organisations that are outside the state and market. It leads UNDP's global work on private sector and foundations and supports UNDP's offices all over the world. UNDP has adopted a Digital Strategy, aiming to better harness technology and innovation to deliver more and better results in the countries we serve. For example, hundreds of partners across the globe supported the MY World survey (2013-2015) that collected almost 10 million votes in the run-up to the adoption of the 2030 Agenda, informing it with people's priorities for the 'world we want'. Persistent poverty and rising inequalities; rapid population growth and demographic transitions - including ageing; migration and urbanisation; environmental degradation and climate change; shifting trends in development cooperation and financing for development; as well as rapid technological advancements, with the associated opportunities and challenges - are all realities of our times. Digital Transformation Pathway 2 is more internally focused and aims to improve the quality, relevance and efficiency, and impact of UNDPs business offering through better knowledge sharing and improved data usage.