Please click the green colored links in the text in order to view highlighted features of the structure. Its protein building blocks have amino acid chains, coiled, cross-linked and classified as either hard or soft. Differences Between Baleen and Toothed Whales. Keratin is the key component of our skin, hair and nails. Scleroproteins are characterized by their long protein filaments. Mol. Octamer: Formed by side-by-side binding of two tetramers containing overall eight keratin molecules. Keratin is a fibrous structural protein found in animal cells and used to form specialized tissues. 2022 Ausmed Education Pty Ltd (ABN: 33 107 354 441). This tutorial will help you understa.. There are different forms of keratin, such as -keratins and harder -keratins. Think you may have COVID-19? 759 lessons, {{courseNav.course.topics.length}} chapters | Keratin fibers are difficult to solubilize and so far it has not been possible to crystallize a whole keratin or a combination of keratin polymers. ThoughtCo, Aug. 27, 2020, thoughtco.com/keratin-definition-and-purpose-608202. 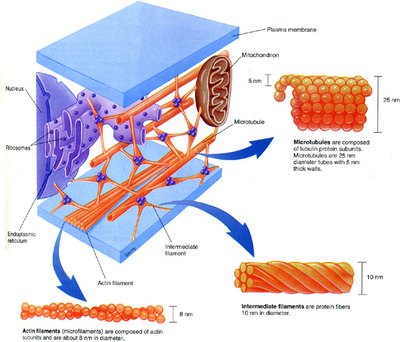 9500 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44195 |. This tutorial describes the sigmoid curve, annual plant growth, tree growth, human growth, and insect growth as the grow.. Neurons generate electric signals that they pass along to the other neurons or target tissues. - Benefits, Foods & Side Effects, What Is Riboflavin?
9500 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44195 |. This tutorial describes the sigmoid curve, annual plant growth, tree growth, human growth, and insect growth as the grow.. Neurons generate electric signals that they pass along to the other neurons or target tissues. - Benefits, Foods & Side Effects, What Is Riboflavin?
If keratinocytes could no longer migrate to the top layer of the epidermis (outer layer of the skin above the dermis), the outer layer of the skin would not be as hard, and the skin would be more susceptible to scrapes and cuts. Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/09/2022.
In the face of this difficulty, soluble segments of keratins have been generated both by proteolytic digestion and gene engineering to study the structural properties of keratins [19] .
Before using our website, please read our Privacy Policy. PDB ID: 3tnu. These two residues define a hydrophobic flank for each protein.
Human genome sequencing revealed that type I and type II keratin genes are located in two clusters each of which includes 27 genes on chromosome 17q21 and on chromosome 12q13 respectively [10] [12]. By contrast, beta-keratins, which occur in birds and reptiles, consist of parallel sheets of polypeptide chains. Type I keratins are generally smaller (average length 460 aa's), and acidic (isoelectric point 4.4-5.4), while type II keratins are longer (average length 545 aa's) and basic (isoelectric point 5-8.3). Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions. succeed. Supplement Scleroproteins or the fibrous proteins are one of the three major types of proteins; the other two are spheroproteins and membrane proteins. Hetero-dimer: Formed by the twining of a matched pair of type I and type II keratins that form a coiled-coil. As a result, your hair turns gray and eventually white. Integumentary System Function & Parts | What is the Integumentary System? The amino acid composition of keratin also varies, depending on the tissue in which it occurs and its function. Cystines are responsible for the great stability of keratin. The epidermis is the top, outermost layer of skin cells. In the K14-K5 dimer only 3-4 residues are involved in inter-strand interactions. There are so many different subjects on Ausmed! The protein is rich in sulfur and insoluble in water.
There are 54 kinds of keratin in your body.
During cornification, keratin fills up the cell resulting in the loss of cytoplasmic organelles and the cessation of metabolism. In a left-handed coiled-coil there are 3.5 residues per turn. The third option noted above is hydrophobic interactions between the two keratins. The purpose of keratin or keratin function includes: What does keratin do for skin? - Causes, Transmission & Symptoms. The IF family of lamins are located on the nuclear lamina and are ubiquitously expressed [3]. As noted above, keratin filaments are composed of hetero-dimers. In this way, cornification can also be a protective mechanism that develops in response to stress. By clicking Accept All Cookies, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. The name "intermediate filament" reflects the comparative morphology of these filaments as their diameter is about 8-12 nm; a value that is "intermediate" between microfilaments with a diameter of 6-7 nm and microtubules with a diameter of 25 nm [8]. 3asw, 4f1z - hKRT10 peptide + clumping factor B, Israel Hanukoglu, Michal Harel, Liora Ezra, Angel Herraez, Categories: Topic Page | Featured in BAMBED, Proteopedia is hosted by the ISPC at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel, Tertiary and quaternary structures of keratins, Bonds that hold the coiled-coil structure, Hydrophobic residues: Main points of contact between chains, Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education, http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2034522100, http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Keratins. By comparative analysis of the predicted structures of a type I keratin, a type II keratin, desmin and vimentin, Hanukoglu and Fuchs suggested that all IF proteins have a central ~310 residue domain that contains four segments in -helical conformation that are separated by three short linker segments predicted to be in beta-turn conformation [5]. The skin thickens and the epidermal cells undergo cornification. Bundles of keratin monomers form what are called intermediate filaments. Keratin protects epithelial cells, strengthens the skin, strengthens internal organs, controls the growth of epithelial cells, and maintains elasticity in the skin. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2386534/). Blisters form as a result of the skin cells separating. The length of keratin fibres depends on their water content: complete hydration (approximately 16 percent water) increases their length by 10 to 12 percent. Human Nervous System Functions & Parts | What Is the Nervous System? What Is a Peptide? These proteins are expressed in epithelial cells and in epidermal cells where they are assembled forming cytoskeletal structures within the cell and epidermal derivatives such as hair, nail and horn [2]. ThoughtCo.
The outermost layer of the skin is called the epidermis.
Keratin filaments may be found in the cornified layer of the skin's epidermis in cells called keratinocytes. The keratin in keratin hair treatments usually comes from ground-up animal parts, so if youre a vegetarian, you may not want to use these products. In this tutorial, you wil.. Physiology is the study of how living organisms function.
Keratin is the name given to a large family of homologous proteins that have a filamentous (fibrous) structure. Animals adapt to their environment in aspects of anatomy, physiology, and behavior. Ionic bonds between charged residues with complementary charge. Though uncommon, keratin hair treatments can sometimes cause hair damage and loss.
Both microfilaments and microtubules are assembled from globular subunits of actin and tubulin respectively.
keratin, fibrous structural protein of hair, nails, horn, hoofs, wool, feathers, and of the epithelial cells in the outermost layers of the skin. Omissions?
Many foods help your body produce keratin. Theyre sometimes called Brazilian blowouts. This tutorial looks at some of the communities in freshwater lentic habitats. Thus, disulfide bridges cannot be responsible for the binding of K14 and K5. Tetramer: Formed by binding of two hetero-dimers in anti-parallel orientation. Sequencing and two dimensional gel electrophoresis of the complete family of keratins revealed that the type I and type II keratins differ in their size and isoelectric points [14] [15]. Fundamental to life, keratin abundant tissue has provided clothing, shelter, adornments, tools and utensils over millennia. This article was most recently revised and updated by, https://www.britannica.com/science/keratin, National Center for Biotechnology Information - PubMed Central - The human keratins: biology and pathology. The only other biological material possessing similar toughness is the protein chitin, found in invertebrates (e.g., crabs, cockroaches).
Get unlimited access to over 84,000 lessons. Educ.[1]. Sebaceous Glands & Sebum | What are Sebaceous Glands? Definition noun, plural: keratins One of the fibrous structural proteins, and is a constituent of hair, nails, skin, feathers, hooves, horns, etc.
Because keratin is not dissolved by digestive acids, ingesting it causes problems in people who eat hair (tricophagia) and results in vomiting of hairballs in cats, once enough hair has accumulated from grooming. Therefore, keratin can remain intact despite exposure to conditions in and outside the human body. What is keratin? The human keratins: biology and pathology. Keratins are grouped into two families termed as type I and type II keratins based on their sequence homology [5]. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. Long-term exposure to formaldehyde may cause cancer. Note: This entry on keratins has been published in Biochem. Example: disulfide S-S bond between two cysteines. The exact mode alignment of the proteins, i.e. lessons in math, English, science, history, and more.
copyright 2003-2022 Study.com. Keratin Overview, Structure & Function | What is Keratin? Beta-keratins are only found in birds and reptiles. For instance, symbiosis occurs in a commun.. Such an octamer is named a.
Unit length filaments (ULF): Formed by lateral - side by side - association of four protofibrils. Getting a keratin hair treatment is a personal decision. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: Verify here. Biol. What is the Function of the Integumentary System? Views expressed here do not necessarily reflect those of Biology Online, its staff, or its partners. Avoiding environments that worsen side effects. Elastin Function & Structure | What is Elastin? - Definition, Foods & Benefits, What Are Complete Proteins? To express the long 2B segment of hetero-dimer of keratins K5 and K14, Lee et al. All Rights Reserved. Beta-keratins are sheets of polypeptide chains that extend in the same directions and never overlap (parallel). Keratins are considered examples of scleroproteins or albuminoids. It is most often found in the epithelial cells of the skin, nails, and hair. These cells are found among other epithelial cells that line the surface of the body. I thought it'd be hard to find the resources I need for complicated procedures or rarer conditions, but they've had everything I've looked for so far. What is the function of keratohyalin granules in the epidermis and where are they located? Keratin can exist as alpha-keratins and beta-keratins according to the configuration of its polypeptide chains (the series of amino acids attached by peptide bonds). Each protein contains its specific order of amino acids, much like each person contains its string of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Covalent bonds. This page, as it appeared on September 12, 2013, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education. Where is keratin found in the skin? What does keratinizing do to an epidermal cell? Keratin's strength and structural integrity make it suitable for withstanding varying environmental conditions.
Disulfide bridges add strength to the protein and contribute to insolubility. Ultimately, the fully keratinized cells undergo a programmed cell death. This includes internal tracts with openings to the outside world like the gastrointestinal and urinary tracts. Thus, in a two chained coiled-coil there is a repeat pattern of seven residues that are represented by the letters a-b-c-d-e-f-g. Residues a and d in this pattern are hydrophobic. Your body naturally produces keratin, and keratin helps form your hair, nails and skin. This seals the keratin solution to your hair. 2, there are two and a single cysteine respectively. The crystal structures of the 2B segment of keratins K14 and K5 provided final confirmation for the role of these hydophobic residues in coiled-coil formation [18]. Skin cells that are constantly exposed to pressure and rubbing leads to the formation of calluses. Soon after, primitive life forms that could assimilate oxygen thrived.. The second option is ionic bonds, or salt bridges between the two keratins. Pancreatic Acinar Cells | Structure & Function, What Is the Pituitary Gland? Working Scholars Bringing Tuition-Free College to the Community, Primary structure: The order of amino acids within one protein molecule, Secondary structure: Amino acids bond together to form an alpha-helix (coil shape) or beta-pleated sheet (accordion shape), Tertiary structure: One portion of a protein chain binds with another portion of the same chain, Quarternary structure: A complex protein structure where more than one protein chain binds to another, Forming the outer layer of the skin that protects organisms from the environment, Maintaining the elasticity and firmness of the skin, Controlling growth and renewal of epithelial cells, Holding skin cells together to form a barrier against bacteria and other organisms, Hyperkeratosis: Excess keratin accumulates either in response to mechanical stress or through a genetic disorder, Keratosis pilaris: Also known as "chicken skin," it accumulates when keratin blocks the pores and clogs hair follicles, Actinic keratosis: Pre-cancerous lesions form on the skin and take on the appearance of sandpaper, Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis: A genetic condition that causes blistering and thickening of the skin, Lichen planus: An overproduction of keratin in the body that causes inflammatory rough patches on the arms and legs, Protect epithelial cells and strengthen the skin, Form an outer protective layer to help organism withstand their environment, Control the growth and renewal of epithelial cells, Maintain elasticity and firmness in the skin, Hold skin cells together with the help of desmosomes.